Problem Definition
- Input: A sequence of $n$ numbers $(a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n)$
- Output: A permutation $(a_1', a_2', \dots, a_n')$ of the input sequence such that $a'_1 \le a'_2 \le \cdots \le a'_n$
Overview
| Algorithm | Worst-case running time | Average-case/expected running time |
|---|---|---|
| insertion sort | $Θ(n^2)$ | $Θ(n^2)$ |
| Merge Sort | $Θ(n\log n)$ | $Θ(n\log n)$ |
| Heapsort | $O(n\log n)$ | - |
| Quicksort | $Θ(n^2)$ | $Θ(n\log n)$ (expected) |
| Counting sort | $Θ(k+n)$ | $Θ(d(n+k))$ |
| Bucket sort | $Θ(n^2)$ | $Θ(n) (average-case) |
$Θ(n^2)$ Sorting Algorithms
Insertion Sort
- sorted sequence를 하나 두고 기존 set에서 하나씩 뽑아 ordered position에 insert
for j = 2 to A.length
key = A[j]
// insert A[j] into the sorted sequence A[i..j-1]
i = j - 1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A[i + 1] = A[i]
i = i - 1
A[i + 1] = key
$Θ(n\log n)$ Sorting Algorithms
Merge Sort
- Divide and Conquer algorithm
merge_sort(arr, l, r):
if l < r
m = (l + r) // 2
merge_sort(arr, l, m)
merge_sort(arr, m+1, r)
merge(arr, l, m, r)
merge(arr, l, m, r):
lp = rp = 0
left = arr[l : m+1] + [inf]
right = arr[m+1 : r+1] + [inf]
for i = l to r:
if left[lp] <= right[rp]:
arr[i] = left[lp]
lp++
else:
arr[i] = right[rp]
rp++
- 체크할 점은, 그냥 l에서 r까지 한쪽 index가 먼저 끝났을 때 overflow될 수 있으므로 마지막에 $\infty$를 추가한다는 점이다.
- time complexity
- $c$는 문제가 straightforward해지도록 하는 constant이다.
- $D(n)$은 dividing problem, $C(n)$은 combine solution이다.
- 각각 $Θ(n)$으로 tight bound된다.
- $aT(n/b)$에서 $n^{\log_b a}$의 $a=b=2$이다.
- 따라서 master theorem에 의해 time complexity는 $Θ(n\log n)$으로 bound된다.
Python code
(boj 2751)[https://github.com/csjihwanh/ps-python/blob/main/boj/2751.py]
Heap Sort
- binary tree인 heap을 사용하는 sorting algorithm이다.
- max heap property를 유지하며 binary tree를 구성한다.
- max-heap property: $A[parent(i)]\ge A[i]$
- insert는 $O(\lg n)$이다.
Max Heapify
- max-heapify는 array가 max-heap property를 만족하도록 만드는 과정이다.
max_heapify(arr, i):
l = left_tree(i)
r = right_tree(i)
if l <= len(arr) and arr[l] > arr[i]:
max = l
else:
max = i
if r <= len(arr) and arr[r] > arr[max]:
max = r
if max != i
swap(arr[i], arr[max])
max_heapify(arr, max)
- input으로는 array와 index $i$가 들어온다.
- left_tree와 right_tree로 얻은 child는 이미 max-heap property를 만족한다고 가정한다.
- 만약 violation이 감지되면 recursive하게 arr[i]를 “float down"한다.
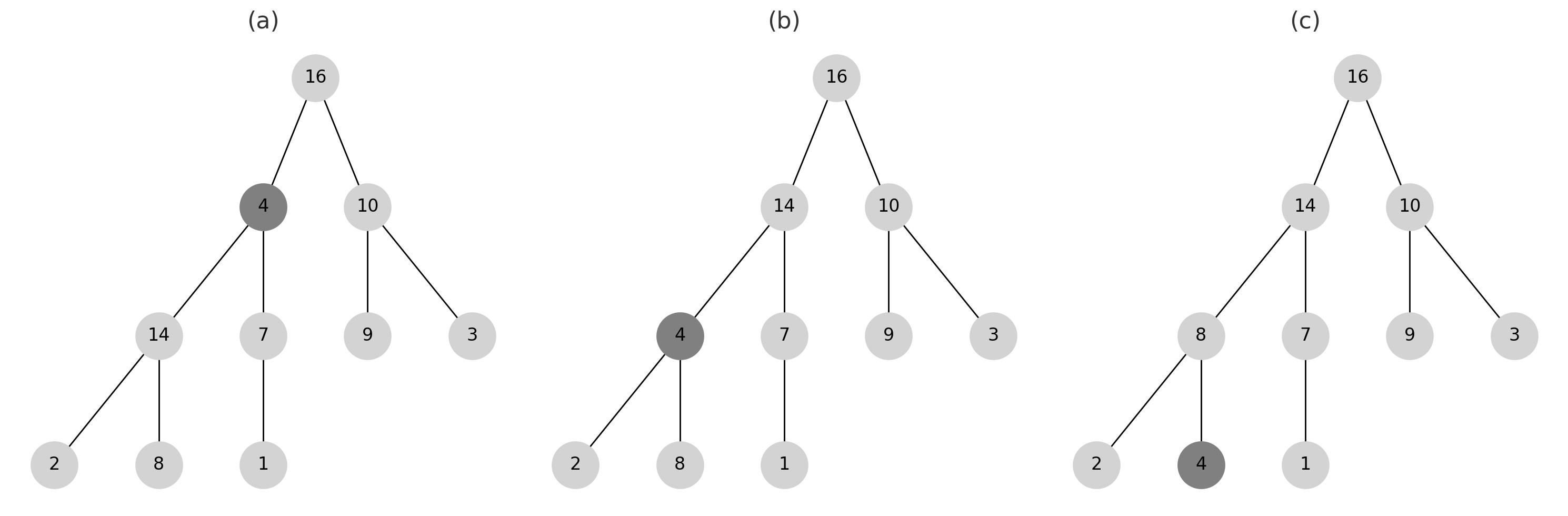
- time complexity는 $T(n)\le T(2n/3)+Θ(1)$이다.
- 왼쪽 subtree가 full인 경우 최대 크기가 $2n/3$이다.
- $a=1, b=3/2$이므로 $n^{\log_{3/2}1}\inΘ(1)$
- master theorem에 의해 $T(n)= Θ(\ln n)$
Building a Heap
- array로부터 heap을 생성하는 bottom-up conversion
build_max_heap(arr):
for i = (len(arr)//2) downto 1:
max_heapify(arr, i)
- Time complexity: $O(n)$
Heapsort
heapsort(arr):
build_max_heap(arr)
for i = len(arr) downto 2:
swap(arr[1], arr[i])
arr = arr[:-1]
max_heapify(arr,1)
- Time complexity: $O(n\lg n)$
Priority Queue
- max값을 $O(\lg n)$에 찾아주는 queue
heap_extract(arr):
if len(arr) < 1:
raise error "heap underflow"
max = arr[1]
arr[1] = arr[len(arr)]
arr = arr[:-1]
max_heapify(arr, 1)
return max
- insert도 $O(\lg n)$에 수행됨.
max_heap_insert(arr, key):
arr = arr + [key]
i = len(arr) - 1
while i > 1:
if arr[parent(i)] < arr[i]:
swap(arr[parent(i)], arr[i])
i = parent(i)
else:
break
Quicksort
- Divide and Conquer 계열 algorithm
- Specification
- worst-case: $Θ(n^2)$
- expected time: $Θ(n\lg n)$
- 다른 algorithm에 비해 $n$ constant가 작아서 빠름.
- memory 적게 사용
- Description
- Divide
- array $A[p\dots r]$를 두 subarray $A[p\dots q-1]$와 $A[q+1\dots r]$로 나눈다.
- $A[q]$ 왼쪽 array의 값들은 $A[q]$보다 작게, 오른쪽은 크게 만든다.
- Conquer
- recursive하게 양쪽 subarray를 conquer한다.
- Combine
- 두 subarrary를 양쪽에 concat한다.
- Divide
quicksort(arr, l, r):
if l < r:
p = partition(arr, l, r)
quicksort(arr, l, p - 1)
quicksort(arr, p + 1, r)
partition(arr, l, r):
x = arr[r]
i = l - 1
for j = l to r - 1:
if arr[j] <= x:
i = i + 1
swap(arr[i], arr[j])
swap(arr[i+1], arr[r])
return i+1
partition- 맨 오른쪽 값을 기준으로, 전체 array에서 맨 오른쪽 값의 위치를 찾는 process
- l부터 i까지는 x보다 작은 값이, i+2부터 r까지는 x보다 큰 값이 위치하게 됨.
- time complexity는 $Θ(r-l+1) =Θ(n)$
Performance of Quicksort
quicksort의 performance는 partitioning의 balance에 따라 좌우됨
balanced partitioning의 경우 $Θ(n\lg n)$을 따르고, unbalanced의 경우 $O(n^2)$을 따름.
Worst-case Partitioning
- 두 subproblem의 크기가 $n-1$과 $0$일때 발생함.
- $T(n) = T(n-1) + T(0) + Θ(n) = T(n-1) + Θ(n)$
- 따라서 $Θ(n^2)$이 됨.
- input array가 completely sorted인 경우 발생.
- 이 경우 insertion sort는 $O(n)$에 해결.
Best-case Partitioning
- 두 subproblem의 크기가 $n/2$보다 크지 않을 때 발생함.
- $T(n) = 2T(n/2) +Θ(n)$
- master theorem에 의해 $T(n) =Θ(n\lg n)$
Balanced Partitioning
- 일반적인 경우에는 $Θ(n\lg n)$에 가까움.
- 항상 9:1로 나눠질 경우
- 각 level은 $cn$ cost를 가짐.
- 가장 짧은 subtree는 $\log_10 n$의 depth, 가장 긴 subtree는 $\log_{10/9} n$의 depth를 가짐.
- $\log_{10/9} n = \frac{\ln n}{\ln (10/9)}$이므로 $Θ(\lg n)$에 asymtotically bound됨.
- 상수이기만 하면 extremely unbalanced한 경우도 $Θ(\lg n)$로 bound됨.
실제 engineering에서는 언제나 input이 random하다고 가정하기 어려우므로, random pivot을 쓸 수 있음.
Python Code
(boj 24090)[https://github.com/csjihwanh/ps-python/blob/main/boj/24090.py]
- 문제 세팅 상 swap을 따로 정의해야 했음.
Refereces
T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson, R. L. Rivest, and C. Stein. Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition. MIT Press, 2009.